Why Gatsby Uses GraphQL
A common question about Gatsby is, “Why does Gatsby use GraphQL? Doesn’t it generate static files?”
Without providing some context, it can seem like GraphQL is overkill for something like Gatsby. In this document, you’ll see what problems arise when creating pages, and how those problems can be solved using GraphQL.
Create a page without any data
Video hosted on egghead.io.
For any kind of pages that aren’t directly created in src/pages/, you’ll need Gatsby’s createPages Node API to create pages programmatically.
All that’s required to create a page is a path where it should be created and the component that should be rendered there.
For example, if you had the following component:
import React from "react"
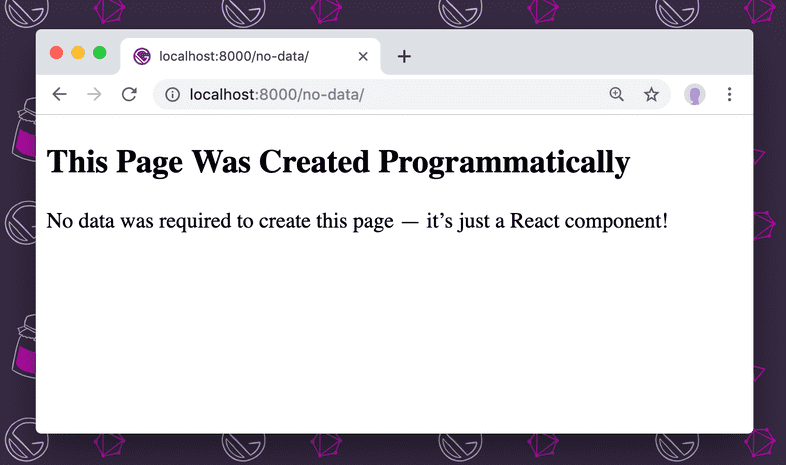
const NoData = () => (
<section>
<h1>This Page Was Created Programmatically</h1>
<p>
No data was required to create this page — it’s just a React component!
</p>
</section>
)
export default NoDataYou could programmatically create a page at /no-data/ by adding the following to gatsby-node.js:
exports.createPages = ({ actions: { createPage } }) => {
createPage({
path: "/no-data/",
component: require.resolve("./src/templates/no-data.js"),
})
}After running gatsby develop, you’ll see the following at localhost:8000/no-data/:
In the simplest cases, this is all that’s required for building pages with Gatsby. However, you’ll often want to pass data to the page so that the template component is reusable.
Create a page with hard-coded data
Video hosted on egghead.io.
To pass data to the created pages, you’ll need to pass context to the createPage call.
In gatsby-node.js, we can add context like so:
exports.createPages = ({ actions: { createPage } }) => {
createPage({
path: "/page-with-context/",
component: require.resolve("./src/templates/with-context.js"),
context: {
title: "We Don’t Need No Stinkin’ GraphQL!",
content: "<p>This is page content.</p><p>No GraphQL required!</p>",
},
})
}The context property accepts an object, and we can pass in any data we want the page to be able to access.
NOTE: There are a few reserved names that cannot be used in
context. They are:path,matchPath,component,componentChunkName,pluginCreator___NODE, andpluginCreatorId.
When Gatsby creates pages, it includes a prop called pageContext and sets its value to context, so we can access any of the values in our component:
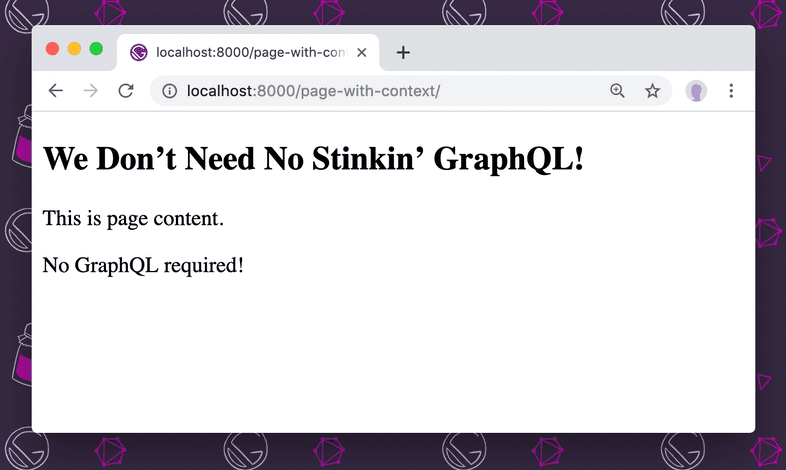
import React from "react"
const WithContext = ({ pageContext }) => (
<section>
<h1>{pageContext.title}</h1>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: pageContext.content }} />
</section>
)
export default WithContextStart the development server with gatsby develop and visit localhost:8000/page-with-context/ to see the created page:
In some cases, this approach may be enough. However, it’s often necessary to create pages from data that can’t be hard-coded.
Create pages from JSON with images
Video hosted on egghead.io.
In many cases, the data for pages can’t feasibly be hard-coded into gatsby-node.js. More likely it will come from an external source, such as a third-party API, local Markdown, or JSON files.
For example, you might have a JSON file with post data:
[
{
"title": "Vintage Purple Tee",
"slug": "vintage-purple-tee",
"description": "<p>Keep it simple with this vintage purple tee.</p>",
"price": "$10.00",
"image": "/images/amberley-romo-riggins.jpg"
},
{
"title": "Space Socks",
"slug": "space-socks",
"description": "<p>Get your feet into these spaced-out black socks with a Gatsby purple border and heel.</p>",
"price": "$10.00",
"image": "/images/erin-fox-and-sullivan.jpg"
},
{
"title": "This Purple Hat Is Blazing Fast",
"slug": "purple-hat",
"description": "<p>Add more blazingly blazing speed to your wardrobe with this solid purple laundered chino twill hat.</p>",
"price": "$10.00",
"image": "/images/david-bailey-cat-hat.jpg"
}
]The images need to be added to the /static/images/ folder. (This is where things start to get hard to manage — the JSON and the images aren’t in the same place.)
Once the JSON and the images are added, you can create product pages by importing the JSON into gatsby-node.js and loop through the entries to create pages:
exports.createPages = ({ actions: { createPage } }) => {
const products = require("./data/products.json")
products.forEach(product => {
createPage({
path: `/product/${product.slug}/`,
component: require.resolve("./src/templates/product.js"),
context: {
title: product.title,
description: product.description,
image: product.image,
price: product.price,
},
})
})
}The product template still uses pageContext to display the product data:
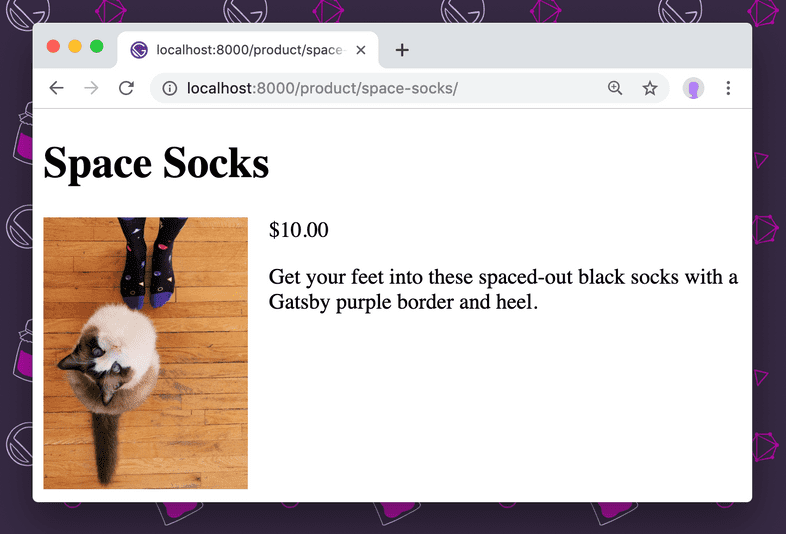
import React from "react"
const Product = ({ pageContext }) => (
<div>
<h1>{pageContext.title}</h1>
<img
src={pageContext.image}
alt={pageContext.title}
style={{ float: "left", marginRight: "1rem", width: 150 }}
/>
<p>{pageContext.price}</p>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: pageContext.description }} />
</div>
)
export default ProductRun gatsby develop, then open localhost:8000/product/space-socks/ to see one of the generated products.
This gets the job done, but it has a few shortcomings that are going to get more complicated as time goes on:
- The images and the product data are in different places in the source code.
- The image paths are absolute from the built site, not the source code, which makes it confusing to know how to find them from the JSON.
- The images are unoptimized, and any optimization you do would have to be manual.
- To create a preview listing of all products, we’d need to pass all of the product info in
context, which will get unweildy as the number of products increases. - It’s not very obvious where data is coming from in the templates that render the pages, so updating the data might be confusing later.
To overcome these limitations, Gatsby introduces GraphQL as a data management layer.
Create pages using GraphQL
There’s a bit more up-front setup required to get data into GraphQL, but the benefits far outweigh the cost.
Using data/products.json as an example, by using GraphQL we’re able to solve all of the limitations from the previous section:
- The images can be colocated with the products in
data/images/. - Image paths in
data/products.jsoncan be relative to the JSON file. - Gatsby can automatically optimize images for faster loading and better user experience.
- We no longer need to pass all product data into
contextwhen creating pages. - Data is loaded using GraphQL in the components where it’s used, making it much easier to see where data comes from and how to change it.
Add the necessary plugins to load data into GraphQL
Video hosted on egghead.io.
In order to load the product and image data into GraphQL, we need to add a few Gatsby plugins. Namely, we need plugins to:
- Load the JSON file into Gatsby’s internal data store, which can be queried using GraphQL (
gatsby-source-filesystem) - Convert JSON files into a format we can query with GraphQL (
gatsby-transformer-json) - Optimize images (
gatsby-plugin-sharp) - Add data about optimized images to Gatsby’s data store (
gatsby-transformer-sharp)
In addition to the plugins, we’ll use gatsby-image to display the optimized images with lazy loading.
Install these packages using the command line:
npm install --save gatsby-source-filesystem gatsby-transformer-json gatsby-plugin-sharp gatsby-transformer-sharp gatsby-imageThen add them to gatsby-config.js:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
{
resolve: "gatsby-source-filesystem",
options: {
path: "./data/",
},
},
"gatsby-transformer-json",
"gatsby-transformer-sharp",
"gatsby-plugin-sharp",
],
}To check that this worked, let’s use the GraphQL Playground, which is available during development, by running:
GATSBY_GRAPHQL_IDE=playground gatsby developNOTE: The
GATSBY_GRAPHQL_IDE=playgroundpart of this command is optional. Adding it enables the GraphQL Playground instead of GraphiQL, which is an older interface for exploring GraphQL.
You can explore the available data schema using the “Docs” tab at the right.
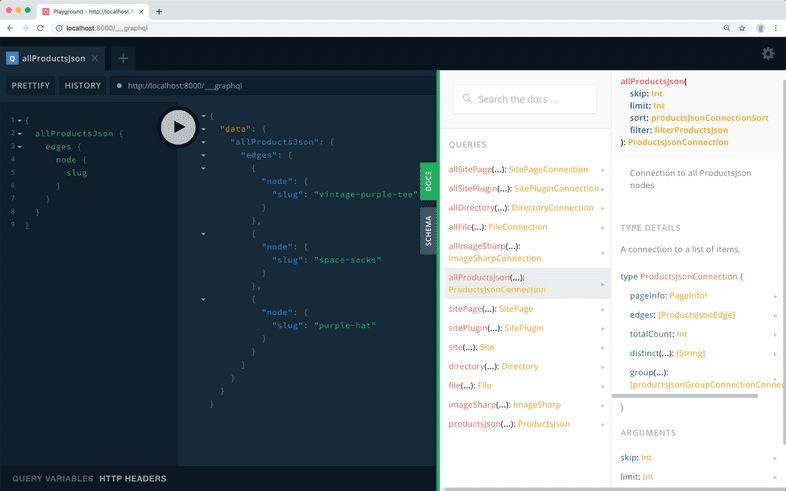
One of the available options is allProductsJson, which contains “edges”, and those contain “nodes”.
The JSON transformer plugin has created one node for each product, and inside the node we can select the data we need for that product.
You can write a query to select each product’s slug like this:
{
allProductsJson {
edges {
node {
slug
}
}
}
}Test this query by entering it into the left-hand panel of the GraphQL Playground, then pressing the play button in the top center.
The results will appear in the panel between the query and the docs, and they’ll look like this:
Generate pages with GraphQL
Video hosted on egghead.io.
In gatsby-node.js, we can use the GraphQL query we just wrote to generate pages.
exports.createPages = async ({ actions: { createPage }, graphql }) => {
const results = await graphql(`
{
allProductsJson {
edges {
node {
slug
}
}
}
}
`)
results.data.allProductsJson.edges.forEach(edge => {
const product = edge.node
createPage({
path: `/gql/${product.slug}/`,
component: require.resolve("./src/templates/product-graphql.js"),
context: {
slug: product.slug,
},
})
})
}You need to use the graphql helper that’s available to the createPages Node API to execute the query. To make sure that the result of the query comes back before continuing, use async/await.
The results that come back are very similar to the contents of data/products.json, so you can loop through the results and create a page for each.
However, note that you’re only passing the slug in context — you’ll use this in the template component to load more product data.
As you’ve already seen, the context argument is made available to the template component in the pageContext prop. To make queries more powerful, Gatsby also exposes everything in context as a GraphQL variable, which means you can write a query that says, in plain English, “Load data for the product with the slug passed in context.”
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
import React from "react"
import { graphql } from "gatsby"
import Image from "gatsby-image"
export const query = graphql`
query($slug: String!) {
productsJson(slug: { eq: $slug }) {
title
description
price
image {
childImageSharp {
fluid {
...GatsbyImageSharpFluid
}
}
}
}
}
`
const Product = ({ data }) => {
const product = data.productsJson
return (
<div>
<h1>{product.title}</h1>
<Image
fluid={product.image.childImageSharp.fluid}
alt={product.title}
style={{ float: "left", marginRight: "1rem", width: 150 }}
/>
<p>{product.price}</p>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: product.description }} />
</div>
)
}
export default ProductA few notes about this file:
- The result of the query is added to the template component as the
dataprop. - The image path was automatically converted by the Sharp transformer into a “child node” that includes optimized versions of the image.
- The query uses a GraphQL fragment to query all the required data for optimized images. GraphQL fragments do not work in the GraphQL Playground.
- The
imgtag has been swapped out for agatsby-imagecomponent namedImage. Instead of asrcattribute, it accepts an object with optimized image data.
Save this file, run gatsby develop, then open localhost:8000/gql/purple-hat/:
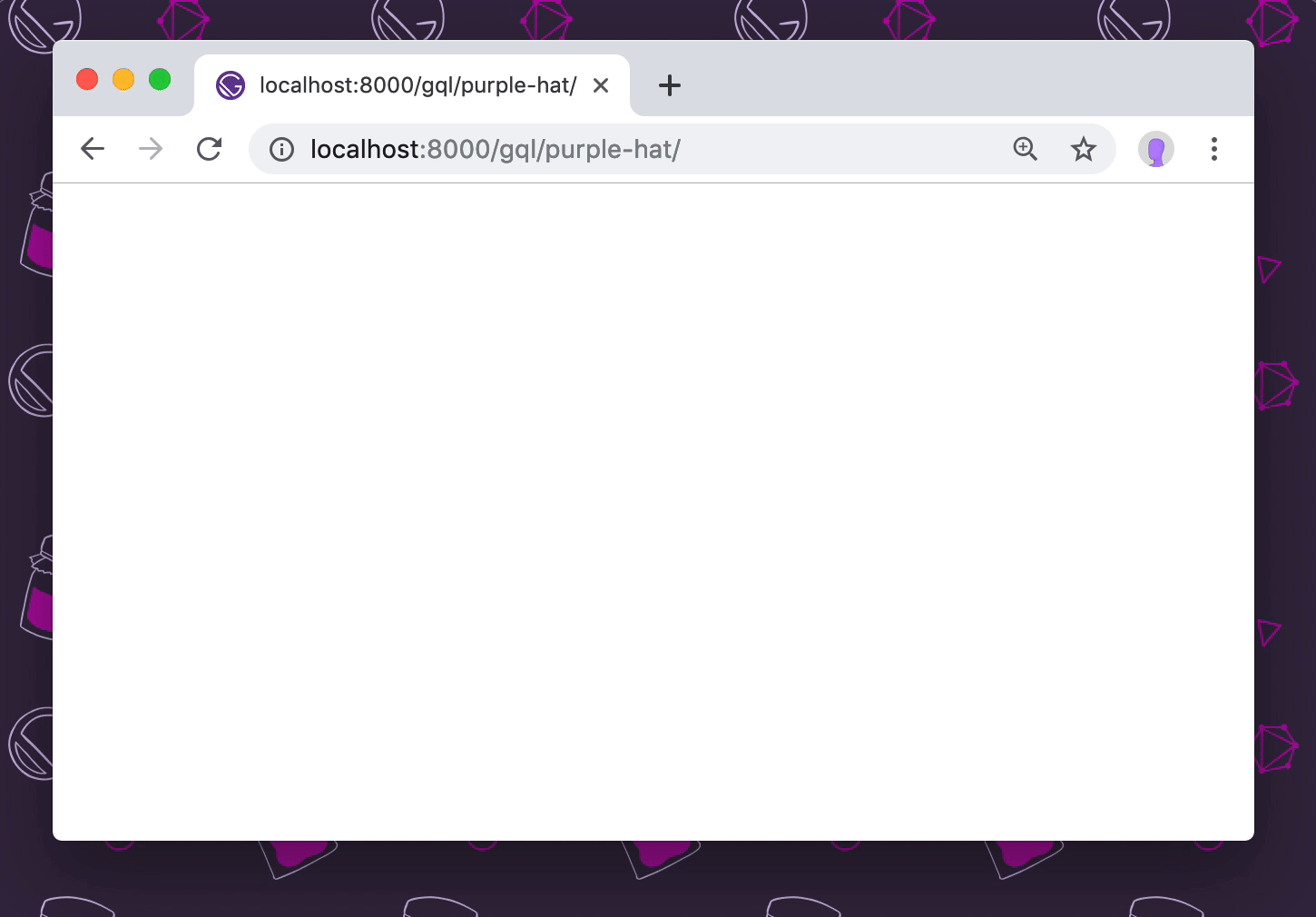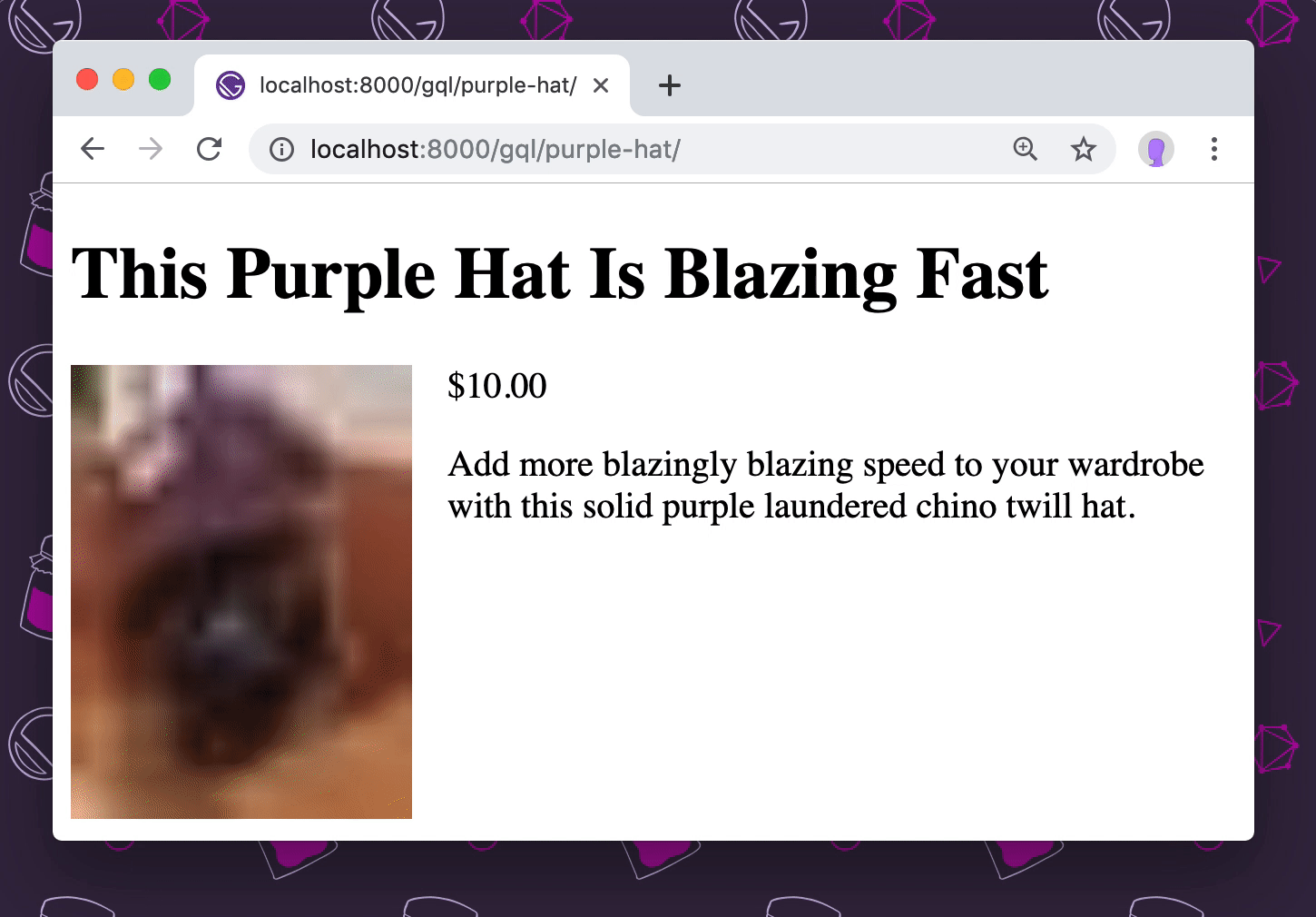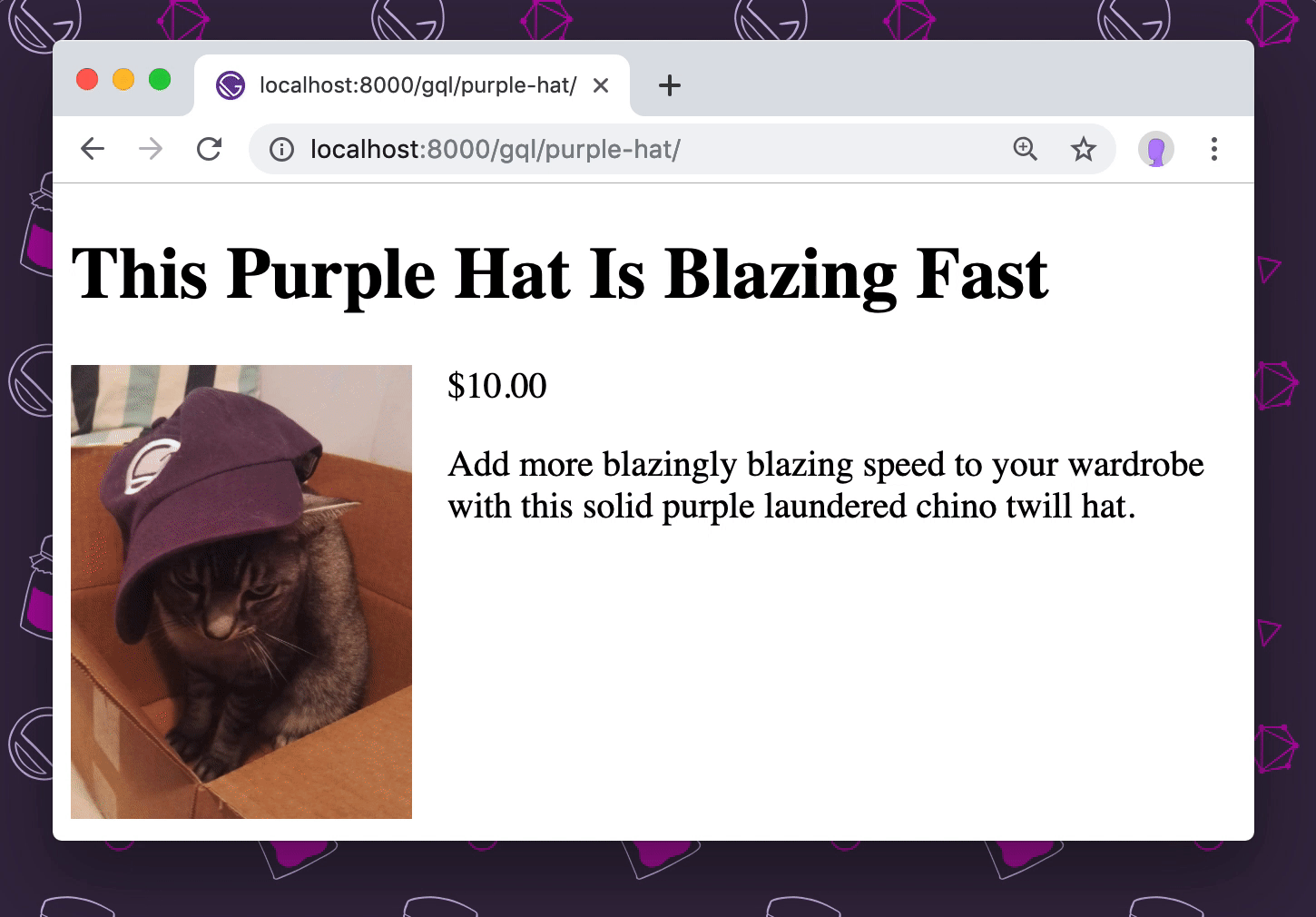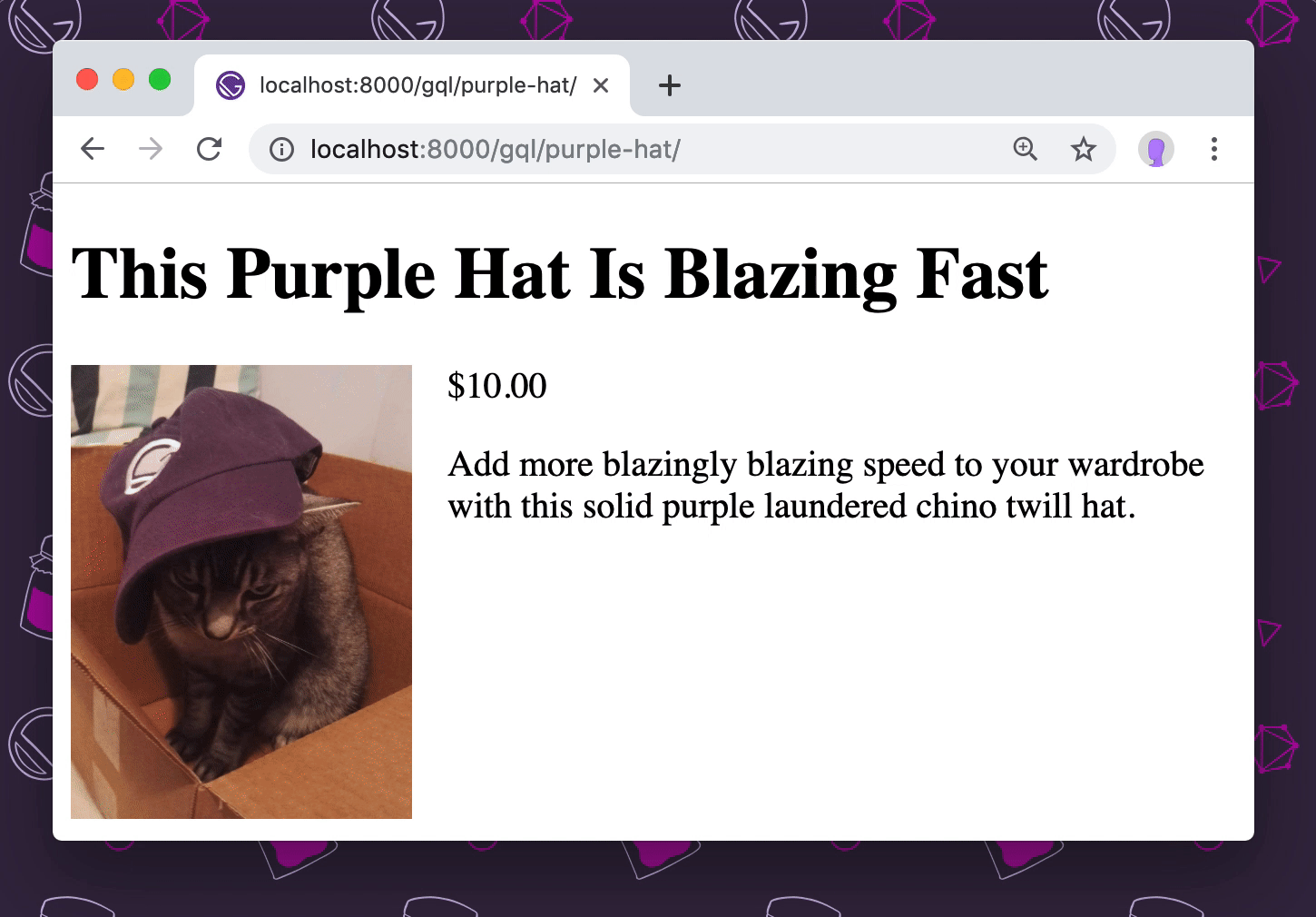
The image is now optimized and lazy loaded.
After the initial setup, loading data with GraphQL is fairly similar to directly loading JSON, but it provides extra benefits like automatically optimizing images and keeping the data loading in the same place where it’s used.
GraphQL is certainly not required, but the benefits of adopting GraphQL are significant. GraphQL will simplify the process of building and optimizing your pages, so it’s considered a best practice for structuring and writing Gatsby applications.
Edit this page on GitHub